
- JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL HOW TO
- JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL CODE
- JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL MAC
- JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL WINDOWS
Use the right-hand menu to navigate.) How Jupyter Notebooks work (This tutorial is part of our Apache Spark Guide.
JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL HOW TO
Yet, how can we make a Jupyter Notebook work with Apache Spark? In this post, we will see how to incorporate Jupyter Notebooks with an Apache Spark installation to carry out data analytics through your familiar notebook interface. When considering Python, Jupyter Notebooks is one of the most popular tools available for a developer. Spark offers developers the freedom to select a language they are familiar with and easily utilize any tools and services supported for that language when developing. Unlike many other platforms with limited options or requiring users to learn a platform-specific language, Spark supports all leading data analytics languages such as R, SQL, Python, Scala, and Java. All these capabilities have led to Spark becoming a leading data analytics tool.įrom a developer perspective, one of the best attributes of Spark is its support for multiple languages. Moreover, Spark can easily support multiple workloads ranging from batch processing, interactive querying, real-time analytics to machine learning and graph processing. Spark utilizes in-memory caching and optimized query execution to provide a fast and efficient big data processing solution.
Refer to this blog article Five tips to get you started with Jupyter notebooks to get further understanding on patterns to follow while using Jupyter notebooks.Apache Spark is an open-source, fast unified analytics engine developed at UC Berkeley for big data and machine learning.
JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL MAC
Accessing Help > Keyboard shortcuts from a running notebook will bring up a help dialog as shown below.Īmong the shortcuts, ctrl + shift + P or cmd + shift + P on a mac is particularly useful as it brings up a command palette into which you can type what you wish to do and execute it. As you get used to this new interface, you can enhance your productivity by learning a few keyboard shortcuts. You can get a tour of the notebook interface from the Help -> User Interface Tour menu. In the screenshot above, note the icons of currently running notebooks are green in color. To do so, from the Notebook Dashboard page, click on the 'New' button and select a Python kernel of choice as shown in the image below.Īlternately, you can create new notebooks from the 'File' menu of a running notebook. In addition to running the sample notebooks, you can create new notebooks for your projects. When a cell is executing the cell number turns to an asterisk (*) and the circle next to the kernal name (Python 3 in the gif above) turns solid. The animation below shows these steps in action. Alternately, you can run a cell using the keyboard shortcut shift + enter. You can run each cell by selecting it and clicking on the 'run cell' button. This opens the notebook in a new tab or window. In the Jupyter Notebook, you can navigate the folder structure and click on a sample notebook. The page you see in this image is called the Notebook Dashboard. The command starts Jupyter Notebook and opens it in your default web browser as shown below.


In the example above, the samples have been downloaded and extracted into c:\code directory. If you are running a sample notebook for the API, you need to 'cd' into the directory where you downloaded the samples. For more information on the benefits of using environments and how to create and manage them, refer to this official documentation page.
If you installed the ArcGIS API for Python in a conda environment other than root (which is the default), you need to activate that environment before starting the Jupyter Notebook.
JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL WINDOWS
Below is a screen shot of how it would appear if you were running the command from Windows command prompt. Similarly if you are running a Mac or Linux OS, this could be your terminal. If you are running a Windows OS, this could be your command prompt or PowerShell window. Once conda and the ArcGIS API for Python is installed, you can start the Jupyter Notebook environment by typing the following command in your terminal. Starting the Jupyter Notebook environment Refer to the official Jupyter documentation and this quick start guide for further details.
JUPYTER NOTEBOOK OPEN IN TERMINAL CODE
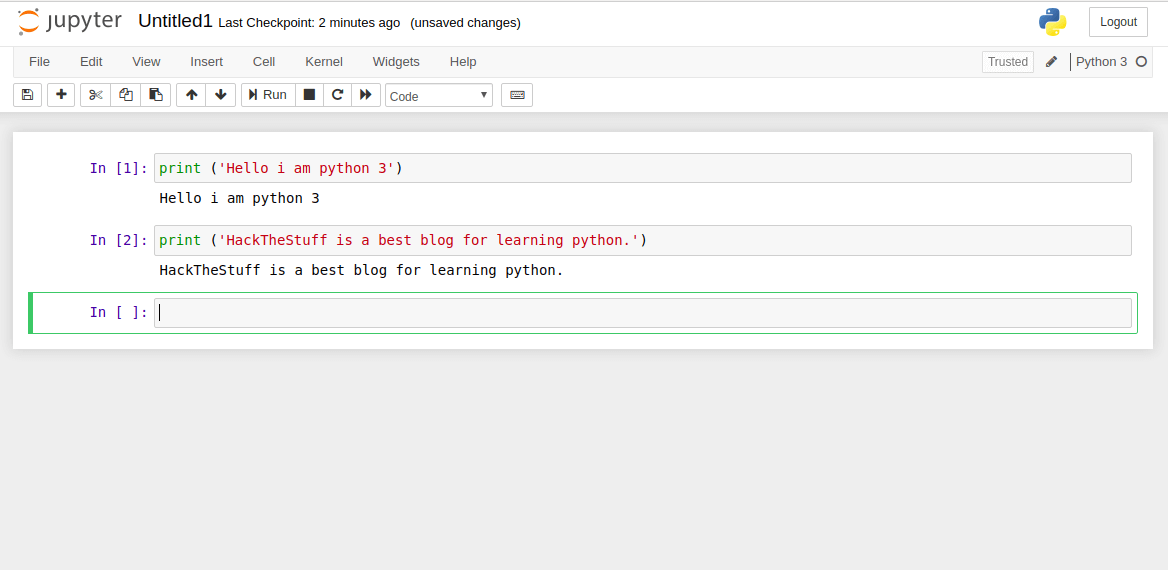
This section provides a quick introduction to the Jupyter Notebook environment where you can run Python code in an interactive manner and visualize the output as maps and charts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
